结肠癌是消化系统最常见的恶性肿瘤之一。统计数据[1]显示,结肠癌的发病率位居全球恶性肿瘤的第3位,致死率位居全球恶性肿瘤的第2位。由于缺乏早期临床症状及特异性分子标志物等因素,大多数结肠癌患者在疾病诊断时即为中晚期,临床预后较差。因此,寻找特异性分子标志物对于制定新的治疗策略和改善结肠癌患者预后具有重要意义。
长链非编码RNA(long noncoding RNA, lncRNA)是指不编码蛋白质且长度超过200个核苷酸的RNA分子[2-3]。LncRNA通过调控RNA转录、染色质修饰、RNA剪接等进而调节基因的表达。lncRNA广泛参与多种肿瘤的发生发展,如肺癌、乳腺癌、前列腺癌、胃癌等[4-7]。
N6-甲基腺苷(N6-methyladenosine, m6A)修饰是指RNA分子腺苷酸第6位氮原子上发生的甲基化修饰,是细菌和真核生物中最丰富的转录后修饰之一,介导细胞多种生物学功能[8-9]。m6A修饰蛋白包括m6A甲基转移酶、m6A去甲基化酶以及m6A甲基结合蛋白。因此,m6A修饰是一种可逆的、动态的转录后修饰过程。m6A修饰能够通过多种途径参与RNA合成和代谢,如RNA剪接、核输出、RNA稳定性、翻译等,从而影响机体的生理反应及疾病状态[10-11],并且在肿瘤的发生发展中起到重要作用[12-14]。
代谢重编程是肿瘤细胞的重要生物学特征之一。为了满足肿瘤快速生长的能量需求,肿瘤细胞通过增强葡萄糖摄取能力及联合脂肪酸代谢等多种能量代谢改变来适应肿瘤微环境[15-16]。脂肪酸是合成细胞生物膜的基本原料和主要能量来源,并且可作为信号分子维持细胞内环境稳态。
近年来的研究[17-19]显示,多种异常表达的m6A相关lncRNA以及脂肪酸代谢相关lncRNA在肿瘤生长增殖、侵袭转移、凋亡及耐药等方面发挥重要作用。然而,有关lncRNA m6A修饰及脂肪酸代谢在结肠癌预后中作用的研究多集中于单个lncRNA功能,不具备独立的预测价值。因此,联合m6A修饰-脂肪酸代谢-lncRNA在预测结肠癌患者预后方面具有更大的价值。本研究通过生物信息学方法分析结肠癌中m6A-脂肪酸代谢相关lncRNA模型及其与结肠癌患者预后的关系,旨在为结肠癌的诊治和预后判断提供依据。
1 材料与方法 1.1 资料来源自TCGA数据库(https://portal.gdc.cancer.gov/)下载结肠癌患者的RNA转录组数据及相关临床信息。其中结肠癌样本483个、正常标本41个。基于已发表的文献[20-21],获取22个被广泛报道的m6A修饰基因(METTL3、METTL14、METTL16、RBM15、WTAP、RBM15B、ZC3H13、YTHDF1、YTHDF2、YTHDF3、YTHDC1、YTHDC2、IGF2BP1、IGF2BP2、IGF2BP3、HNRNPC、HNRNPA2B1、ALKBH3、ALKBH5、FTO、RBMX、EIF3A)。CIBERSORT分析结果下载自https://gdc.cancer.gov/about-data/publications/panimmune。图 1示研究流程。
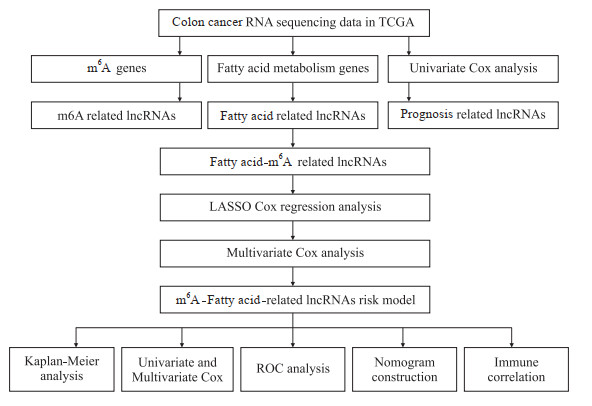
|
| 图 1 研究流程图 Fig 1 Workflow of the study |
在R软件(v3.6.3)中,采用m6A修饰基因与lncRNA共表达方法分析m6A修饰基因与lncRNA的相关性,将相关系数>0.4且P<0.001的lncRNA定义为m6A相关lncRNA;采用脂肪酸代谢基因与lncRNA共表达方法分析脂肪酸代谢基因和lncRNA的相关性,将相关系数>0.4且P<0.001的lncRNA定义为脂肪酸代谢相关lncRNA。两者的交集为m6A-脂肪酸代谢相关lncRNA。在此基础上分析结肠癌患者的生存状态和生存时间,最终得到具有结肠癌预后预测意义的m6A-脂肪酸代谢相关lncRNA。
1.3 风险评分模型构建对上述筛选出的lncRNA进行LASSO回归(least absolute shrinkage and selection operator)及多因素Cox回归分析,构建m6A-脂肪酸代谢相关lncRNA的结肠癌风险评分模型。采用风险评分公式对上述相关系数进行加权计算,最终确定此模型的风险评分。风险评分=ΣβlncRNA×ExplncRNA(βlncRNA为与生存相关的lncRNA的系数,ExplncRNA为样本中每个lncRNA的表达量)。根据风险评分将结肠癌患者分为低风险组及高风险组。
1.4 风险评分模型验证采用Kaplan-Meier生存曲线分析高风险组与低风险组患者的总生存期。利用单因素及多因素Cox回归影响结肠癌患者预后的因素。用ROC评价风险模型的预测价值;通过构建列线图,评估模型预测患者1年、3年、5年的生存率,确定风险模型预测预后的准确性。
1.5 免疫相关通路及其与风险评分模型的相关性分析将高风险组与低风险组患者的差异基因进行基因本体(gene ontology, GO)分析及基因富集(gene set enrichment analysis, GSEA)分析。采用CIBERSORT算法对结肠癌组织RNA-seq数据进行反卷积(deconvolution)计算,评估免疫细胞的浸润及免疫检查点基因表达情况[22]。
1.6 统计学处理采用R软件(v3.6.3)进行统计分析,采用Wilcoxon秩和检验进行组间比较;单因素、多因素Cox回归分析结肠癌患者总生存期的相关因素。分别用glmnet和survival包进行LASSO回归及Kaplan-Meier生存分析。用timeROC包分析ROC曲线下面积(AUC);用Regplot包绘制列线图。检验水准(α)为0.05。
2 结果 2.1 结肠癌患者m6A-脂肪酸代谢相关lncRNA的鉴定 2.1.1 结肠癌与癌旁组织中总体差异lncRNA从TCGA数据中获取了4 345个lncRNA的表达数据。根据设定的显著性阈值,发现共有1 797个lncRNA在结肠癌和癌旁组织中存在有统计学意义的差异表达,其中在结肠癌组织中表达上调者有1 537个、下调者有260个(图 2)。

|
| 图 2 结肠癌和癌旁组织中差异lncRNA(火山图) Fig 2 Volcano plot of differential lncRNAs between the colon cancer and adjacent tissues |
Pearson相关分析(相关系数>0.4,P<0.001)共鉴定出670个m6A相关lncRNA及1 011个脂肪酸代谢相关lncRNA;单因素Cox回归分析显示,39个m6A-脂肪酸代谢相关lncRNA与结肠癌患者预后相关(图 3A)。图 3B、图 3C展示了这39个lncRNA与患者临床特征及m6A修饰基因表达的相关性。
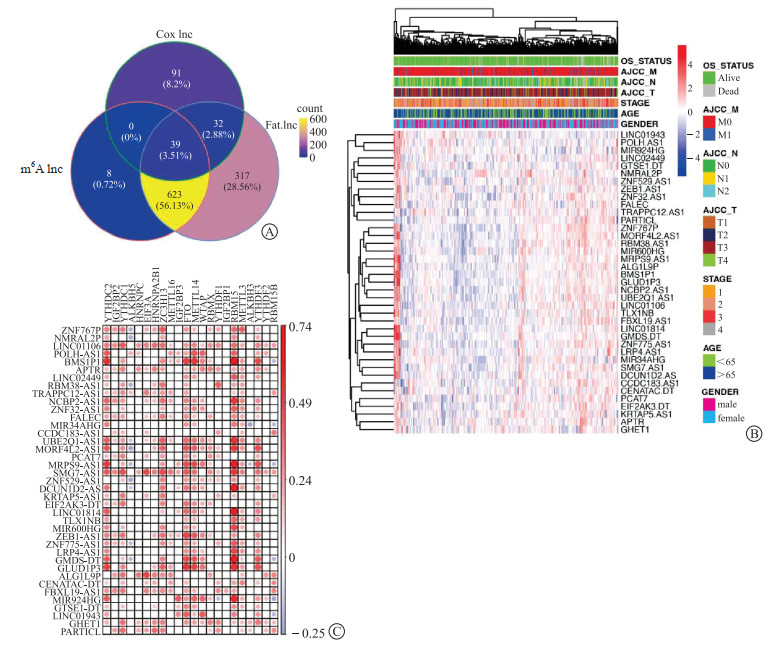
|
| 图 3 结肠癌m6A-脂肪酸代谢相关lncRNA筛选及相关性分析 Fig 3 Screening and correlation analysis of lncRNAs related to m6A-fatty-acid-metabolism in colon cancer A: m6A and/or fatty-acid-metabolism-related lncRNAs in colon cancer selection; B: Correlations between m6A-fatty-acid-metabolism-related lncRNAs and clinical features; C: Correlations between m6A modification genes and m6A-fatty-acid-metabolism-related lncRNAs. |
通过LASSO回归分析,筛选出18个与结肠癌患者预后相关的lncRNA(图 4A、4B)。多因素回归分析(图 4C)发现,POLH-AS1、FALEC、MIR34AHG、ZNF529-AS1以及MIR924HG是影响结肠癌患者预后的独立因素(P<0.05)。其中,POLH-AS1[1.472(1.138, 1.833) vs 1.062(0.832, 1.171)]、FALEC[0.734(0.373, 1.226) vs 0.351(0.262, 0.529)]、MIR34AHG[1.447(0.999, 1.993) vs 0.472(0.360, 0.666)]、MIR924HG[0.458(0.246, 0.712) vs 0.249(0.197, 0.330)]表达在结肠癌组织较癌旁正常组织中升高(P<0.05,图 4D)。根据风险评分结果,将结肠癌患者分为高风险组及低风险组。
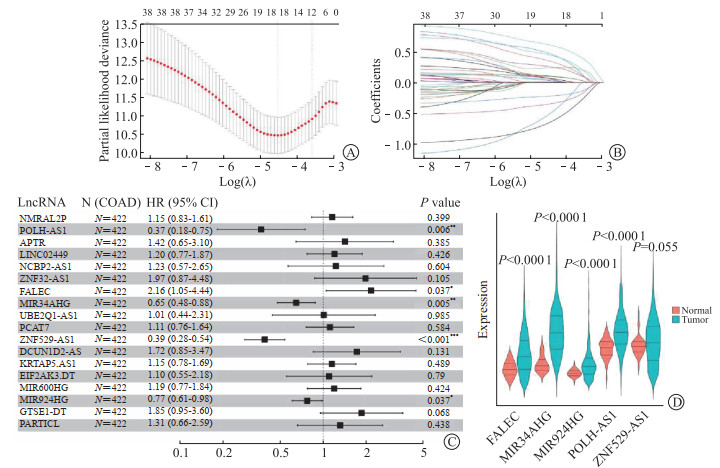
|
| 图 4 结肠癌m6A-脂肪酸代谢相关lncRNA风险模型构建 Fig 4 Construction of m6A-fatty-acid-metabolism-related lncRNA risk model in colon cancer A: The LASSO Cox regression analysis was carried out to construct a risk model. The best parameter (λ) was selected based on the LASSO model; B: 18 lncRNAs were screened by LASSO regression analysis according to the best λ; C: Multivariate Cox regression model based on 18 m6A-fatty-acid-metabolism-related lncRNAs; D: Analysis of differentially expressed lncRNAs in colon cancer and normal tissues. |
高风险组及低风险组两组患者的生存状态及lncRNA表达差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05,图 5A)。Kaplan-Meier生存分析结果显示,高风险组结肠癌患者的总生存期短于低风险组(P<0.000 1,图 5B)。
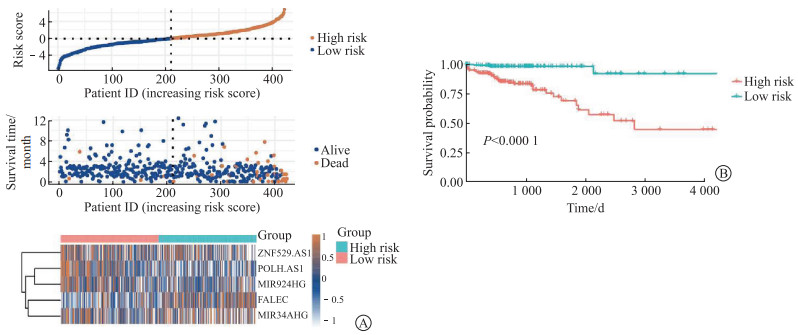
|
| 图 5 结肠癌m6A-脂肪酸代谢相关lncRNA风险模型评分与生存预后相关性分析 Fig 5 The correlation between m6A-fatty-acid-metabolism-related lncRNA risk score and prognosis in colon cancer A: Distributions of risk scores, survival status, and expression levels of lncRNAs of patients in different groups; B: Kaplan-Meier plots for comparing overall survival between low-risk and high-risk groups. |
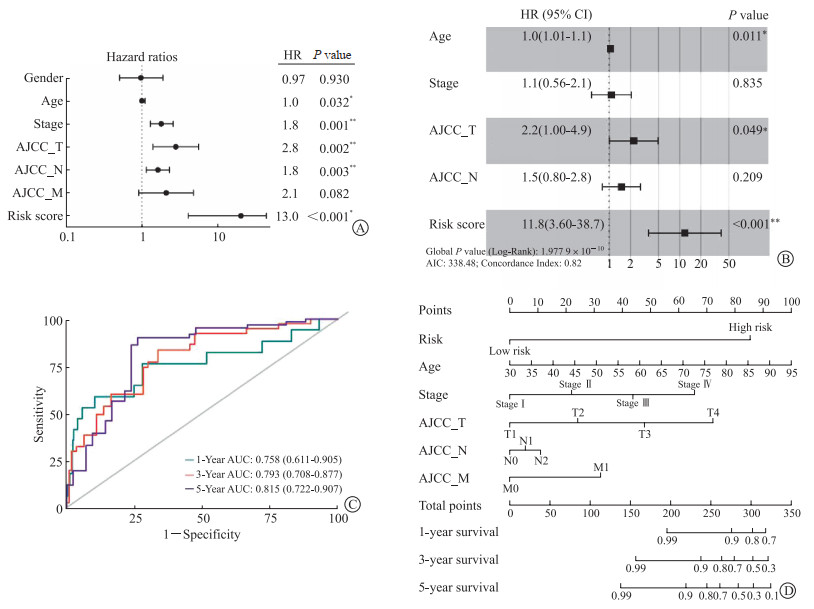
单因素及多因素Cox回归分析显示,风险模型评分是影响结肠癌患者预后的独立因素(P<0.001,图 6A、6B)。ROC曲线(图 6C)显示,风险模型评分对患者1年、3年、5年生存率的预测价值较高,AUC分别为0.758 (95%CI 0.611~0.905)、0.793 (95%CI 0.708~0.877)、0.815 (95%CI 0.722~0.907)。基于风险模型评分、年龄、AJCC分期、分级构建列线图,用以预测结肠癌患者1年、3年、5年总生存率,显示出较好的预测能力(图 6D)。
|
| 图 6 风险评分模型的预后预测评价 Fig 6 Evaluation of the risk model for prognosis prediction in colon cancer A, B: Univariate and multivariate Cox regression analysis were conducted to screen the independent risk factors affecting prognosis of colon cancer patients; C: ROC curves of the risk score were conducted to predict overall survival in colon cancer; D: Nomograms for predicting overall survival probability of colon cancer patients. |
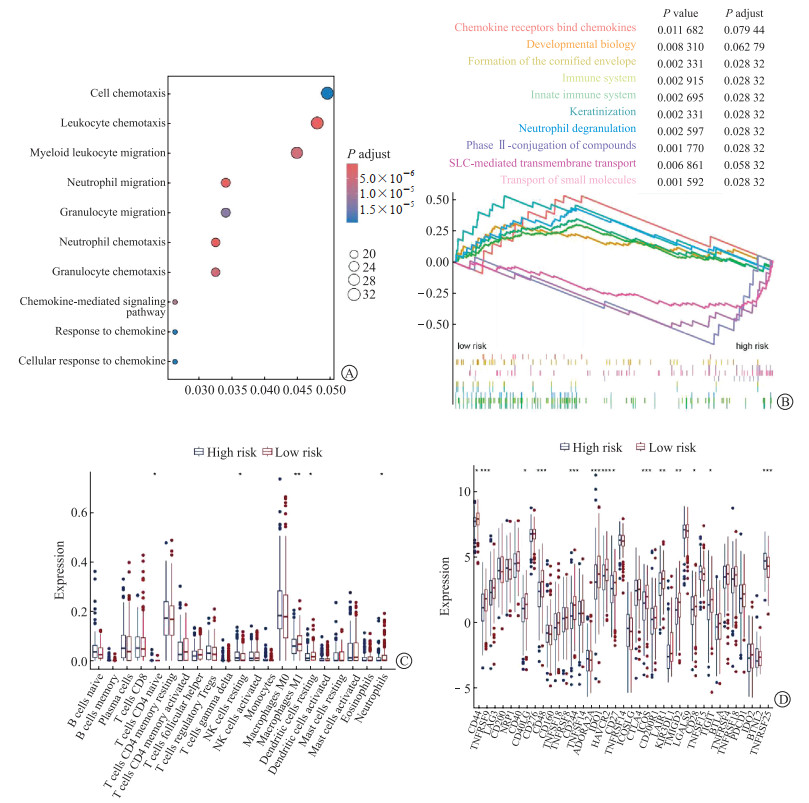
GO分析(图 7A)显示,中性粒细胞迁移、白细胞趋化等通路显著富集;GSEA分析表明,免疫调节通路、先天性免疫系统、中性粒细胞脱颗粒等通路在低风险组中显著富集(图 7B)。CIBERSORT算法计算结果显示,低风险组患者肿瘤组织中有更多的M1型巨噬细胞浸润,高风险组患者则有更多的静止NK细胞(图 7C);低风险组中免疫检查点基因(CD44、TNFRSF9、CD40LG、CD48、CD244、IDO1、HAVCR2、CD27、ICOS、LAIR1、TMIGD2、CD28和TIGIT)表达较高(P<0.05,图 7D)。由此推测,m6A-脂肪酸代谢相关lncRNA风险模型评分较低的结肠癌患者对免疫治疗可能更为敏感。
|
| 图 7 风险模型与肿瘤免疫微环境的相关性 Fig 7 Correlation between risk model and tumor immune microenvironment A: Significantly enriched GO pathways of different expressed genes between high and low-risk groups; B: Gene sets enriched in high and low-risk groups; C: The proportions of immune cells in high-risk and low-risk groups; D: Expressions of genes related to the immune response in high-risk and low-risk groups. |
表观遗传修饰是指细胞核DNA序列不改变的情况下,基因功能发生的可逆、可遗传的改变,包括组蛋白修饰、甲基化修饰和非编码RNA[23-26]等。m6A修饰是最常见和最丰富的RNA修饰形式之一,其通过m6A去甲基化酶、m6A甲基转移酶和m6A结合蛋白在肿瘤发展中起关键作用[27-28]。m6A能调控lncRNA的表达,从而影响肿瘤的发生发展。例如:m6A修饰的lncRNA BCAN-AS1作为支架促进c-Myc和SNIP1形成三元复合物,抑制c-Myc泛素化和降解,从而促进胰腺癌细胞的生长和转移[29];RNA m6A介导的lncRNA BLACAT3表达上调能招募YBX3进入细胞核,协同增强NCF2转录,进而促进膀胱癌血管生成和血液转移[30]。同时,基于m6A相关基因的癌症预测模型构建也逐渐成为肿瘤风险评估领域的热点。Feng等[31]成功构建了m6A相关lncRNA风险模型,用于预测膀胱癌患者预后、免疫疗效和化疗反应;Li等[32]采用生物信息学方法筛选出m6A相关lncRNA和mRNA,揭示了结直肠癌发生和进展的潜在机制,为结直肠癌预后评估及临床诊治提供了新的靶点。
肿瘤发生发展过程中常伴有代谢改变。肿瘤细胞主要通过有氧糖酵解来获取快速增殖所需的能量[33]。除糖酵解外,肿瘤细胞还需进行脂肪酸代谢来合成癌细胞生长所需的脂膜和信号分子。脂肪酸代谢联合糖代谢等方式进行代谢重编程,以适应肿瘤的快速增长[34-35]。LncRNA NEAT1能激活c-Jun/c-Fos/SREBP1通路,促进脂肪酸代谢,从而增强胃癌的淋巴结转移能力[36];METTL5介导的m6A修饰能增加肝癌细胞脂肪酸代谢并促进肿瘤发生[37]。然而,m6A修饰、lncRNA及脂肪酸代谢三者在肿瘤发生发展中协同作用的研究仍较少。
本研究通过LASSO回归分析、Cox回归分析筛选出5个能独立预测结肠癌患者预后的m6A-脂肪酸代谢相关lncRNA:POLH-AS1、FALEC、MIR34AHG、ZNF529-AS1及MIR924HG。既往研究发现,这些lncRNA与肿瘤的发生发展密切相关:POLH-AS1作为一种铁死亡相关lncRNA,与原发性肝细胞癌患者的预后相关[38];FALEC通过竞争性结合miR-203b上调PIM3,促进胃癌细胞增殖及转移[39];Bai等[40]发现,MIR34AHG作为m5C相关lncRNA,是肺腺癌患者的独立预后因素,并与肿瘤微环境重塑相关;ZNF529-AS1通过增加FBXO31表达促进肝癌细胞侵袭和转移[41];在子宫内膜癌中,MIR924HG表达上调,并且与肿瘤化疗耐药相关[42]。本研究ROC分析结果提示,基于上述lncRNA所构建的预后风险模型预测患者1年、3年、5年生存率的AUC较大。
免疫治疗疗效和肿瘤免疫浸润密切相关。M1型巨噬细胞能抑制NF-κB通路,进而延缓肿瘤进展[43]。NK细胞是先天免疫系统的细胞毒性淋巴细胞,能快速杀死肿瘤细胞。NK细胞介导的免疫疗法首先用于治疗晚期白血病,目前已成为免疫治疗的主要方法[44]。本研究中,低风险组结肠癌患者组织中有更多的M1型巨噬细胞浸润,而高风险组患者组织中有更多的静止NK细胞浸润,同时低风险组免疫检查点基因表达较高。该结果提示,相较于高风险组,风险模型评分低的结肠癌患者对免疫治疗的反应更好,表明该模型可为结肠癌患者免疫治疗提供指导。
综上所述,本研究首次建立了m6A-脂肪酸代谢相关lncRNA模型,并证明其可用于预测结肠癌患者预后。分析免疫微环境发现,该风险模型评分与免疫细胞浸润及免疫检查点基因表达相关。本研究所建立的m6A-脂肪酸代谢相关lncRNA风险预测模型有助于预测结肠癌患者的预后及免疫疗效。
伦理声明 无。
利益冲突 所有作者声明不存在利益冲突。
作者贡献 沈超琴:数据下载、分析及作图;刘韬韬:研究设计及文章撰写。
| [1] |
SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL R L, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 209-249.
[DOI]
|
| [2] |
QUINN J J, CHANG H Y. Unique features of long non-coding RNA biogenesis and function[J]. Nat Rev Genet, 2016, 17(1): 47-62.
[DOI]
|
| [3] |
ENGREITZ J M, OLLIKAINEN N, GUTTMAN M. Long non-coding RNAs: spatial amplifiers that control nuclear structure and gene expression[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2016, 17(12): 756-770.
[DOI]
|
| [4] |
HE Y M, JIANG X L, DUAN L C, et al. LncRNA PKMYT1AR promotes cancer stem cell maintenance in non-small cell lung cancer via activating Wnt signaling pathway[J]. Mol Cancer, 2021, 20(1): 156.
[DOI]
|
| [5] |
ZENG H, HOU Y X, ZHOU X Y, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts facilitate premetastatic niche formation through lncRNA SNHG5-mediated angiogenesis and vascular permeability in breast cancer[J]. Theranostics, 2022, 12(17): 7351-7370.
[DOI]
|
| [6] |
ZHANG B Y, ZHANG M P, SHEN C Y, et al. LncRNA PCBP1-AS1-mediated AR/AR-V7 deubiquitination enhances prostate cancer enzalutamide resistance[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2021, 12(10): 856.
[DOI]
|
| [7] |
LUO Y H, ZHENG S T, WU Q Y, et al. Long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) EIF3J-DT induces chemoresistance of gastric cancer via autophagy activation[J]. Autophagy, 2021, 17(12): 4083-4101.
[DOI]
|
| [8] |
WANG X, LU Z K, GOMEZ A, et al. N6-methyladenosine-dependent regulation of messenger RNA stability[J]. Nature, 2014, 505(7481): 117-120.
[DOI]
|
| [9] |
WANG X, ZHAO B S, ROUNDTREE I A, et al. N(6)-methyladenosine modulates messenger RNA translation efficiency[J]. Cell, 2015, 161(6): 1388-1399.
[DOI]
|
| [10] |
RIES R J, ZACCARA S, KLEIN P, et al. m6A enhances the phase separation potential of mRNA[J]. Nature, 2019, 571(7765): 424-428.
[DOI]
|
| [11] |
SHU L Q, HUANG X L, CHENG X J, et al. Emerging roles of N6-methyladenosine modification in neurodevelopment and neurodegeneration[J]. Cells, 2021, 10(10): 2694.
[DOI]
|
| [12] |
AN Y Y, DUAN H. The role of m6A RNA methylation in cancer metabolism[J]. Mol Cancer, 2022, 21(1): 14.
[DOI]
|
| [13] |
CHANG G Q, SHI L, YE Y Q, et al. YTHDF3 induces the translation of m6A-enriched gene transcripts to promote breast cancer brain metastasis[J]. Cancer Cell, 2020, 38(6): 857-871.e7.
[DOI]
|
| [14] |
HUANG H L, WENG H Y, CHEN J J. m6A modification in coding and non-coding RNAs: roles and therapeutic implications in cancer[J]. Cancer Cell, 2020, 37(3): 270-288.
[DOI]
|
| [15] |
DEY P, KIMMELMAN A C, DEPINHO R A. Metabolic codependencies in the tumor microenvironment[J]. Cancer Discov, 2021, 11(5): 1067-1081.
[DOI]
|
| [16] |
PAVLOVA N N, ZHU J J, THOMPSON C B. The hallmarks of cancer metabolism: still emerging[J]. Cell Metab, 2022, 34(3): 355-377.
[DOI]
|
| [17] |
CUI Y B, ZHANG C Y, MA S S, et al. RNA m6A demethylase FTO-mediated epigenetic up-regulation of LINC00022 promotes tumorigenesis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2021, 40(1): 294.
[DOI]
|
| [18] |
YIN J X, DING F S, CHENG Z C, et al. METTL3-mediated m6A modification of LINC00839 maintains glioma stem cells and radiation resistance by activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2023, 14(7): 417.
[DOI]
|
| [19] |
DONG H L, ZENG L L, CHEN W W, et al. N6-methyladenine-mediated aberrant activation of the lncRNA SOX2OT-GLI1 loop promotes non-small-cell lung cancer stemness[J]. Cell Death Discov, 2023, 9(1): 149.
[DOI]
|
| [20] |
ZHANG L L, HOU C F, CHEN C, et al. The role of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification in the regulation of circRNAs[J]. Mol Cancer, 2020, 19(1): 105.
[DOI]
|
| [21] |
CHEN K P, SHI Y, ZHU H J. Analysis of the role of glucose metabolism-related genes in dilated cardiomyopathy based on bioinformatics[J]. J Thorac Dis, 2023, 15(7): 3870-3884.
[DOI]
|
| [22] |
CHEN B B, KHODADOUST M S, LIU C L, et al. Profiling tumor infiltrating immune cells with CIBERSORT[J]. Methods Mol Biol, 2018, 1711: 243-259.
|
| [23] |
杨志文, 阿古达木, 韩怡茹, 等. MiR-494-3p/RRS1轴对结直肠癌影响作用及机制[J]. 临床军医杂志, 2022, 50(4): 389-393. YANG Z W, A G D M, HAN Y R, et al. Effect and mechanism of miR-494-3p/RRS1 axis on colorectal cancer[J]. Clin J Med Off, 2022, 50(4): 389-393. [CNKI] |
| [24] |
常旭东, 李宏宇, 陈江, 等. 长链非编码RNA GAS5对胰腺癌AsPC-1细胞凋亡、迁移及侵袭能力调控作用[J]. 临床军医杂志, 2022, 50(6): 599-602. CHANG X D, LI H Y, CHEN J, et al. Effects of long non-coding RNA GAS5 on apoptosis, migration and invasion of pancreatic cancer AsPC-1 cells[J]. Clin J Med Off, 2022, 50(6): 599-602. [CNKI] |
| [25] |
范华, 易亭伍, 马闻, 等. 食管癌组织miR-452-5p、SOX7表达及与病理参数和预后关系[J]. 疑难病杂志, 2022, 21(12): 1271-1276. FAN H, YI T W, MA W, et al. Expression of miR-452-5p and SOX7 in esophageal carcinoma and their relationship with pathological parameters and prognosis[J]. Chin J Difficult Complicat Cases, 2022, 21(12): 1271-1276. [DOI] |
| [26] |
杨理超, 吴国涛, 吴强, 等. m6A RNA甲基化修饰在炎症性肠病中的研究进展[J]. 中华炎性肠病杂志(中英文), 2022, 6(2): 174-178. YANG L C, WU G T, WU Q, et al. Research progress of m6A RNA methylation modification in inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Chin J Inflamm Bowel Dis, 2022, 6(2): 174-178. [CNKI] |
| [27] |
WANG Y M, WANG Y, PATEL H, et al. Epigenetic modification of m6A regulator proteins in cancer[J]. Mol Cancer, 2023, 22(1): 102.
[DOI]
|
| [28] |
CAO X X, GENG Q S, FAN D P, et al. m6A methylation: a process reshaping the tumour immune microenvironment and regulating immune evasion[J]. Mol Cancer, 2023, 22(1): 42.
[DOI]
|
| [29] |
WU G D, SU J C, ZENG L X, et al. LncRNA BCAN-AS1 stabilizes c-Myc via N6-methyladenosine-mediated binding with SNIP1 to promote pancreatic cancer[J]. Cell Death Differ, 2023, 30(10): 2213-2230.
[DOI]
|
| [30] |
XIE J B, ZHANG H, WANG K Y, et al. m6A-mediated-upregulation of lncRNA BLACAT3 promotes bladder cancer angiogenesis and hematogenous metastasis through YBX3 nuclear shuttling and enhancing NCF2 transcription[J]. Oncogene, 2023, 42(40): 2956-2970.
[DOI]
|
| [31] |
FENG Z H, LIANG Y P, CEN J J, et al. m6A-immune-related lncRNA prognostic signature for predicting immune landscape and prognosis of bladder cancer[J]. J Transl Med, 2022, 20(1): 492.
[DOI]
|
| [32] |
LI W, GAO Y C, JIN X J, et al. Comprehensive analysis of N6-methylandenosine regulators and m6A-related RNAs as prognosis factors in colorectal cancer[J]. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids, 2022, 27: 598-610.
[DOI]
|
| [33] |
VANDER HEIDEN M G, DEBERARDINIS R J. Understanding the intersections between metabolism and cancer biology[J]. Cell, 2017, 168(4): 657-669.
[DOI]
|
| [34] |
CURRIE E, SCHULZE A, ZECHNER R, et al. Cellular fatty acid metabolism and cancer[J]. Cell Metab, 2013, 18(2): 153-161.
[DOI]
|
| [35] |
KOUNDOUROS N, POULOGIANNIS G. Reprogramming of fatty acid metabolism in cancer[J]. Br J Cancer, 2020, 122(1): 4-22.
[DOI]
|
| [36] |
JIA Y X, YAN Q, ZHENG Y L, et al. Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 mediated RPRD1B stability facilitates fatty acid metabolism and lymph node metastasis via c-Jun/c-Fos/SREBP1 axis in gastric cancer[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2022, 41(1): 287.
[DOI]
|
| [37] |
PENG H, CHEN B B, WEI W, et al. N6-methyladenosine (m6A) in 18S rRNA promotes fatty acid metabolism and oncogenic transformation[J]. Nat Metab, 2022, 4(8): 1041-1054.
[DOI]
|
| [38] |
FANG C K, LIU S L, FENG K L, et al. Ferroptosis-related lncRNA signature predicts the prognosis and immune microenvironment of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Sci Rep, 2022, 12(1): 6642.
[DOI]
|
| [39] |
DONG W J, GONG M C, XIAO J J, et al. Long non-coding RNA (FALEC) promotes malignant behaviors of gastric cancer cells by regulating miR-203b/PIM3 axis[J]. Ann Transl Med, 2022, 10(10): 579.
[DOI]
|
| [40] |
BAI M, SUN C. m5C-related lncRNA predicts lung adenocarcinoma and tumor microenvironment remodeling: computational biology and basic science[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2022, 10: 885568.
[DOI]
|
| [41] |
MA Y, SUN W L, MA S S, et al. LincRNA ZNF529-AS1 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma via FBXO31 and predicts the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma patients[J]. BMC Bioinformatics, 2023, 24(1): 54.
[DOI]
|
| [42] |
ZHOU X Y, ZHANG H, DUAN Y C, et al. m6A-related long noncoding RNAs predict prognosis and indicate therapeutic response in endometrial carcinoma[J]. J Clin Lab Anal, 2023, 37(1): e24813.
[DOI]
|
| [43] |
DAN H X, LIU S, LIU J J, et al. RACK1 promotes cancer progression by increasing the M2/M1 macrophage ratio via the NF-κB pathway in oral squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Mol Oncol, 2020, 14(4): 795-807.
[DOI]
|
| [44] |
MYERS J A, MILLER J S. Exploring the NK cell platform for cancer immunotherapy[J]. Nat Rev Clin Oncol, 2021, 18(2): 85-100.
[DOI]
|
 2024, Vol. 31
2024, Vol. 31


